Introduction:
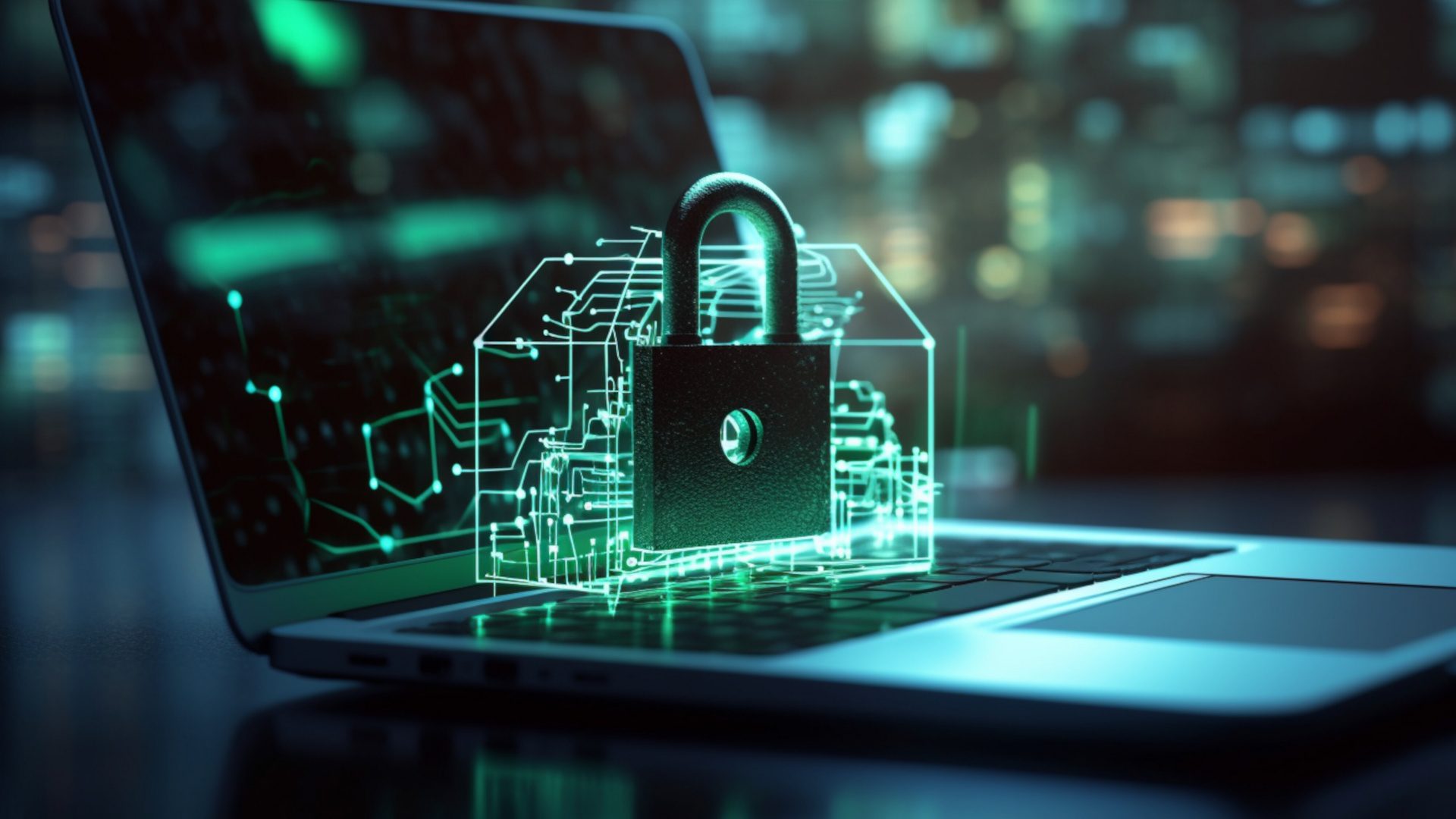
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technology, the increasing reliance on mobile devices has made cybersecurity a critical concern for users worldwide. With the prevalence of smartphones and tablets running on two dominant platforms – Android and iOS – ensuring the security of personal data and sensitive information has become paramount. This article delves into the intricacies of cybersecurity, exploring key entities such as Android users, iPhone users, Android devices, iOS devices, and the associated ecosystems, shedding light on the various aspects that contribute to a secure digital experience.
Mobile Platforms and Operating Systems:
Mobile platforms, comprising Android and iOS, serve as the foundation for the functionality of smartphones and tablets. Android, known for its open ecosystem, offers users a wide array of customization options, allowing them to tailor their devices to suit personal preferences. On the other hand, iOS, the operating system powering Apple devices, is renowned for its high-level security measures and a closed ecosystem that tightly controls the apps available on the Apple App Store.
App Stores and Security Measures:
The app stores, namely the Google Play Store for Android users and the Apple App Store for iPhone users, play a pivotal role in ensuring the safety of the applications available for download. Both platforms implement stringent security measures to screen and verify the legitimacy of apps, aiming to prevent the infiltration of malicious software. However, the open nature of the Android platform exposes it to potential vulnerabilities, making it imperative for users to exercise caution when downloading apps from third-party sources.
Security Breaches and Updates:
Despite the efforts invested in securing mobile platforms, security breaches are not uncommon. Malicious apps, often disguised as legitimate applications, may find their way onto users’ devices, posing a threat to personal data and privacy. To mitigate these risks, both Android and iOS regularly release security updates, patching critical vulnerabilities and strengthening the overall security of the operating systems. Timely installation of these updates is crucial for users to stay protected against evolving threats.
End-to-End Encryption:
End-to-end encryption stands as a robust security measure that ensures the confidentiality of user communications. Messaging apps on both Android and iOS devices employ end-to-end encryption to safeguard conversations from unauthorized access. This cryptographic technique ensures that only the intended recipient can decipher the messages, providing an additional layer of protection against eavesdropping and data interception.
Third-Party Security Apps and Strong Passwords:
To further fortify the security of their devices, users can leverage third-party security apps. These applications offer additional features such as antivirus scans, malware detection, and anti-phishing tools. Additionally, the adoption of strong, unique passwords is essential for securing accounts and preventing unauthorized access. Both Android and iOS platforms encourage users to create complex passwords and often provide tools for managing and storing these passwords securely.
Apple Fans and iPhone Viruses:
Apple fans, known for their allegiance to the brand, often benefit from the robust security measures integrated into iOS. While iPhone viruses are relatively rare compared to their Android counterparts, it is crucial for users to remain vigilant. The closed ecosystem of iOS, coupled with stringent app vetting processes, contributes to a lower likelihood of encountering malicious software. Nevertheless, users are advised to exercise caution and adhere to best practices for digital security.
Google Play and the Open Ecosystem:
The Google Play Store, as the primary marketplace for Android apps, operates within a more open ecosystem. While this openness provides users with greater customization options, it also introduces potential vulnerabilities. Android users must be discerning when selecting apps and opt for trusted sources to minimize the risk of downloading harmful applications. Google Play’s security protocols aim to identify and remove malicious apps, but users’ awareness and caution remain crucial in maintaining a secure digital environment.
Various Hardware Designs and Encryption Keys:
Android’s diverse ecosystem encompasses a multitude of hardware designs from various manufacturers, offering users a wide range of choices in terms of device features and specifications. However, this diversity also poses challenges for maintaining a standardized level of security across all devices. In contrast, Apple’s iOS operates on a more controlled hardware environment, enabling a streamlined approach to security and updates. Encryption keys, fundamental in securing data, are managed differently on each platform, contributing to their distinct security postures.
iCloud Service vs. Google Stores:
Apple’s iCloud service and Google’s cloud-based solutions play integral roles in securing user data. While iCloud emphasizes privacy by storing user data on Apple’s own servers, Google leverages its cloud infrastructure to provide a seamless and interconnected experience across devices. The debate over centralized versus distributed storage raises questions about data privacy, with personal preferences and trust in the respective companies influencing users’ choices.
Technology Experts and Strong Security:
The collaboration between technology experts and platform developers plays a crucial role in fortifying cybersecurity measures. Continuous research, threat analysis, and the development of innovative security solutions contribute to the evolution of robust security frameworks. Both Apple and Google invest in partnerships with cybersecurity experts, fostering a collaborative approach to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Appropriate Measures and Questionable Legality:
Amidst the efforts to enhance cybersecurity, the debate over the legality of certain measures remains contentious. Apple’s strict app vetting process, while ensuring the security of the App Store, has been criticized for its restrictive nature. On the other hand, Android’s more open approach allows users greater freedom but exposes them to potential risks. Striking a balance between security and user freedom remains a challenge, prompting ongoing discussions within the tech community and among users.
Conclusion:
In the ever-expanding digital landscape, the cybersecurity of mobile devices stands as a critical concern for Android and iPhone users alike. The interplay between mobile platforms, operating systems, app stores, and user practices shapes the overall security of the digital realm. While both Android and iOS offer distinct security features and challenges, users must remain vigilant, adopt best practices, and stay informed about the evolving threat landscape. As technology continues to advance, the collaboration between industry experts, platform developers, and users remains pivotal in safeguarding the integrity and security of personal digital spaces.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours