Introduction:
The fashion industry is a dynamic and ever-evolving entity that reflects societal changes, cultural shifts, and individual expressions of identity. From the early days of basic garments to the modern era of high-tech wearable technology, the journey of fashion has been marked by various trends, controversies, and innovations. In this article, we delve into the multifaceted aspects of the fashion industry, covering everything from historical roots and design evolution to contemporary issues such as sustainability, diversity, and technological integration.
Historical Roots and Evolution:
The history of the fashion industry can be traced back centuries, with each era contributing to the development of distinctive styles and trends. The evolution of fashion design has been propelled by factors such as societal norms, technological advancements, and artistic movements. From the Renaissance period to the Rococo era, and the Industrial Revolution to the roaring twenties, fashion has continually reinvented itself.
In the 21st century, one notable trend that gained prominence was the Y2K aesthetic. The turn of the millennium brought forth a fusion of futuristic designs, metallic fabrics, and bold colors. Y2K fashion, characterized by its daring and unconventional styles, marked a departure from the minimalist trends of the late 20th century. This period saw the rise of unconventional fashion statements, challenging traditional norms and pushing the boundaries of self-expression.
Controversies and Diversity:
The fashion industry has not been without its controversies. One longstanding issue has been the presence of racism in fashion advertisements. Critics argue that the industry often perpetuates racial stereotypes and lacks diversity in its representation of models. Initiatives promoting inclusivity and challenging stereotypes have gained momentum in recent years, urging fashion houses to embrace a broader spectrum of cultures and ethnicities in their campaigns.
One example of cultural appropriation in fashion is the controversy surrounding the qipao, a traditional Chinese dress. Western designers have faced backlash for appropriating the qipao without acknowledging its cultural significance. This raises questions about the responsibility of fashion houses to respect and honor diverse cultural heritage in their designs.
Fast Fashion vs. Sustainable Fashion:
The rise of fast fashion in recent decades has revolutionized the industry, with brands focusing on mass production, quick turnover, and affordability. However, the environmental and ethical implications of fast fashion have come under scrutiny. The industry’s contribution to waste, pollution, and poor working conditions has sparked a growing demand for sustainable fashion alternatives.
Sustainable fashion emphasizes eco-friendly materials, ethical manufacturing processes, and fair labor practices. The concept aligns with the growing awareness of the environmental impact of consumer choices. Many fashion houses are now exploring sustainable practices, embracing the circular economy model to minimize waste and promote the recycling of materials.
Innovations in Fashion Design and Technology:
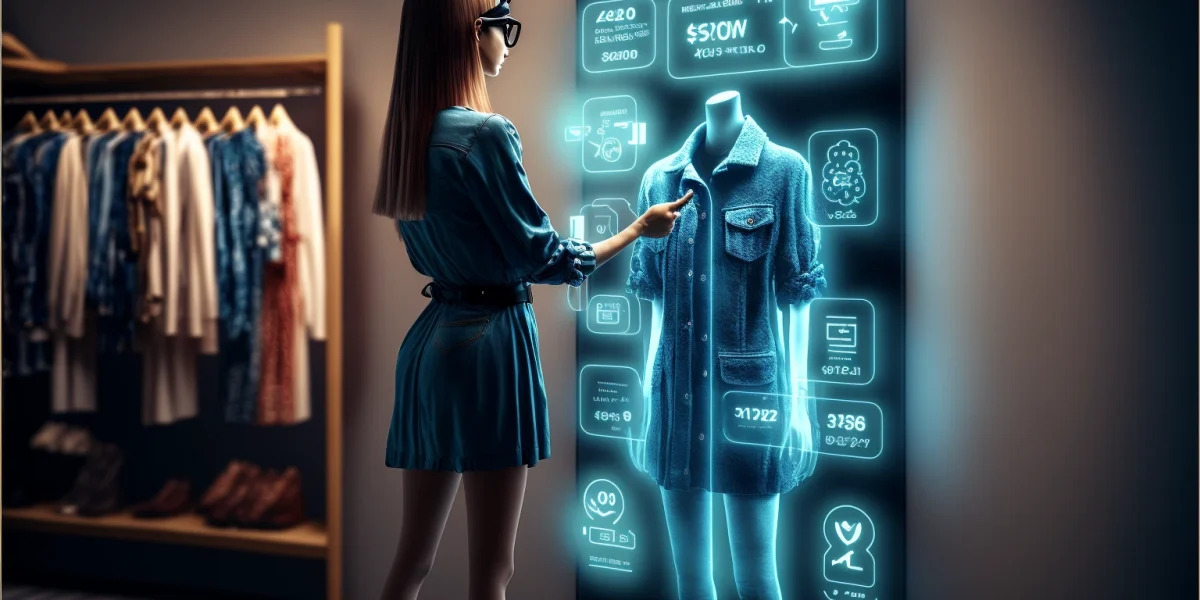
The history of fashion design is intertwined with technological advancements. The advent of sewing machines during the Industrial Revolution revolutionized the production process, making clothing more accessible to the masses. Today, technology continues to shape the industry, with innovations like wearable technology making a significant impact.
Wearable technology integrates functionality and fashion, offering consumers smart clothing and accessories that go beyond mere aesthetics. From fitness trackers embedded in clothing to garments with built-in heating elements, the marriage of fashion and technology is pushing the boundaries of what clothing can achieve.
Public Relations and Market Research:
Fashion houses rely on effective public relations strategies to connect with consumers and shape their brand image. Social media platforms have become powerful tools for fashion PR, allowing brands to engage directly with their audience, showcase their designs, and respond to trends in real-time. This immediate connection has reshaped the traditional fashion communication landscape.
Market research plays a crucial role in shaping fashion trends and consumer preferences. Through focus groups and data analysis, brands gain insights into the ever-shifting demands of their target audience. Understanding market dynamics helps fashion houses stay ahead of trends and cater to the evolving tastes of consumers.
Cultural Influences on Fashion:
Cultural influences play a pivotal role in shaping fashion trends. Traditional garments like the kimono have not only retained their cultural significance but have also influenced global fashion. The fusion of traditional elements with modern design has given rise to unique and eclectic styles, reflecting a globalized fashion landscape.
Street style, characterized by individual expression and grassroots fashion movements, has also become a major influence on mainstream trends. The democratization of fashion through street style has given rise to a diverse range of influences, challenging the dominance of high-end fashion houses.
The Role of Fashion Houses and Brands:
Fashion houses and brands are the driving forces behind the industry, shaping the narrative of each season’s trends. Whether haute couture or ready-to-wear, each brand contributes to the diverse tapestry of styles available to consumers. The growth of a brand often hinges on its ability to adapt to changing tastes, connect with consumers, and maintain a distinct identity.
The design of specific clothing items, such as blouses or V-neck tops, often becomes synonymous with certain brands, contributing to their signature style. A brand’s success is intricately tied to its ability to create a unique identity that resonates with its target audience.
Conclusion:
The fashion industry is a dynamic and multifaceted realm that continually evolves, influenced by historical roots, cultural diversity, technological innovations, and consumer preferences. As the industry moves forward, an increasing focus on sustainability, inclusivity, and the integration of technology is shaping its trajectory. By exploring the complex interplay of entities such as menswear, Y2K aesthetics, racism in fashion advertisements, qipao, fast fashion, sustainable fashion, history of fashion design, fashion trends, circular economy, sewing, wearable technology, public relations, kimono, market research, street style, fashion design, fashion houses, blouses, brands, growth, V-neck styles, and focus groups, we gain a comprehensive understanding of the fascinating world of fashion and its ongoing evolution.





















+ There are no comments
Add yours